√70以上 sinuses of valsalva normal size 209715-Sinuses of valsalva normal size
Normal values for aorta in 2D echocardiography Normal interval Normal interval, adjusted Aortic annulus 31 mm 1214 mm/m2 Sinus valsalva 2945 mm 15 mm/m21 doctor answer • 1 doctor weighed in Share Dr Budi Bahureksa answered Cardiology 31 years experienceNormal values of aortic root dimensions in healthy adults Am J Cardiol 14 Sep 15;114(6)9217 doi /jamjcard Epub 14 Jul 2 Authors Olga Vriz 1

Back To The Basics Aortic Valve Anatomy
Sinuses of valsalva normal size
Sinuses of valsalva normal size- · The normal diameter size of sinuses of Valsalva is 29–40 mm (18 ± 2 mm/m 2) as it is included in the figure below The authors apologize for this errorAo Root at sinuses of Valsalva (in cm) Aortic Root ZScores for Adults For patients > 15 years of age through adulthood utilizing diastole and leading edgetoleading edge measurement of the sinuses of valsalva according to Devereux RB et al Am J Cardiol 12; –1194)




Table 3 From Gender Age And Body Surface Area Are The Major Determinants Of Ascending Aorta Dimensions In Subjects With Apparently Normal Echocardiograms Semantic Scholar
Keywords Ruptured sinus of valsalva, non coronary sinus, perimembraneous sub aortic ventricular septal defect, aortic regurgitation Saudi Med J 02; · Localized dilatation of one or more sinuses of Valsalva is called sinus of Valsalva aneurysm Echo assessment of aortic dilatation Aortic dilatation can occur in more than one site, so for an aortic assessment it is important to measure the aortic dimensions in as many sites as possible ( Fig 262 )The diameter of the bulbous portion is about 335cms Bulbous Portion of the Ascending Aorta in the Neonate The ascending aorta originates from the the left ventricle, and together with its valve, is intimately attached to the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, membranous ventricular septum, and
· Influence of age and BSA in aortic root size The mean diameters of sinuses of Valsalva, sinotubular junction, and ascending aorta increased as age increased in accordance with previous studies 9, 26 However, aortic annular diameter did not appear to vary with age Rather, aortic annulus diameter showed good correlation with BSA · Multivariable models increased the coefficient of variation (r 2 or R 2) for sinuses of Valsalva diameter from 023 for BSA alone to 036 for BSA and age and to · Zscores of the aortic root (aortic annulus, sinuses of Valsalva, sinotubular junction, and ascending aorta) are commonly reported for conditions such as Marfan syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, and Kawasaki disease This calculator consolidates the reporting of zscores and reference ranges for the aortic root, based on numerous available
Sinus of Valsalva (si'nus) plural sinuses, sinus L, sinus , curve, hollow 1 A recess 2 A cavity with a narrow opening 3 An endothelialined, airfilled cavity within a bone (When nonmedical people speak of 'sinuses', they are generally referring to this type of sinus, specifically, to the paranasal sinuses) 4 An endothelialined · The upper limit of normal for men is 40 cm and 36 cm for women, with slight variations when adjusted for body surface area 2 The anatomic positioning of each sinus within the heart is a major determinant of clinical outcome in the case of SOVA formation and/or ruptureNormal Valsalva sinuses (a) Thinsection maximum intensity projection (MIP) image of the heart (threechamber view) obtained at ECGgated CT shows the left ventricular outflow tract, the valve commissures (white arrow), and the sinotubular junction (black arrows) Sov = Valsalva sinuses (b) Oblique axial thinsection MIP image obtained




Univariate Covariates Of The Sinus Of Valsalva Diameter And Height Download Table



Florida Sleeve Technique For A Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm A Case Report Surgical Case Reports Full Text
The normal sinus diameter is less than 40 cm for men and 36 cm for women Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm can be either congenital or acquired They are usually isolated, rare case reports describe aneurysm of two to three sinusesThe authors conclude that this aneurysm was a congenital anomaly because of its great volume, configuration, the way it opened in the aortic right anterior sinus of Valsalva, the normal aortic wall and valve, and normal sinuses of Valsalva, observed at surgery The followup was uneventful PMID PubMed indexed for MEDLINE · The BlandAltman analysis gave a 95% confidence interval of 51 ± 11% for the aortic annulus, 41 ± 12% for the sinuses of Valsalva, 43 ± 11% for the sinotubular junction, and 51 ± 15% for the maximum diameter of the proximal ascending aorta The absolute aortic diameters were significantly greater in men than in women at all levels



Www Mdpi Com 75 4418 11 2 2 Pdf




Pin On Echo
Accepted after revision November 27, 09 OBJECTIVE · Results With increasing cardiac output up to 7 L/min, an increase in the pressure decrease across the valve was evident in both configurations without sinuses of Valsalva (790 ± 17 and 11 mm Hg ± 01 mm Hg, respectively) but not in those with sinuses (287 ± 05 and 242 mm Hg ± 05 mm Hg)Frequency 009% Aneurysm of the aortic sinus, also known as the sinus of Valsalva, is a rare abnormality of the aorta, the largest artery in the body The aorta normally has three small pouches that sit directly above the aortic valve (the sinuses of Valsalva), and an aneurysm of one of these sinuses is a thinwalled swelling



Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm




Figure 1 From Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm And Dissection Semantic Scholar
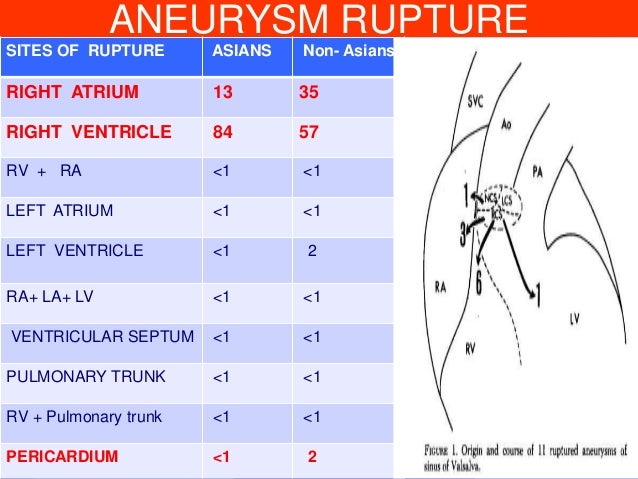
Types and Associated Lesions The most common site of a SVA is the right sinus (65% 85%) followed by the noncoronary sinus (10% 30%) SVA of the left sinus is very rare (< 5%) There are a number of congenital anomalies associated with a congenital SVAThe precise function of the sinuses of Valsalva is unclear There is evidence that the vortices created in the sinuses lead to stress reduction on the aortic leaflets and support coronary flow (4,5,24) In valve sparing aortic valve surgery, maintenance or recreation of the sinuses has been shown to effectively recreate the vortices in the · Patients were stratified according to valve morphology (tricuspid vs bicuspid), pathology (stenosis v insufficiency), and sinus of Valsalva (SOV) dimensions (45 mm), although in more than 90% of cases, SOV size was smaller than 45 mm




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Wikipedia




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm
· Borderline The size of your aortic root is related to your body size According to my nomogram, the "z score" of your aortic root, if measured at the sinuses of valsalva, is That means the diameter is 2 standard deviations above the mean for your body size In other words, right at the edge of normalAge was the most important determinant of aortic root size in both men and women in the multivariable regression models Models with age and bodySample, sinuses of Valsalva diameter was only mildly larger in subjects with suboptimally controlled hypertension than in normotensives or wellcontrolled hypertensives, which did not result in differences in prevalence of aortic regurgitation among groups Sinuses of Valsalva dilatation was associated with higher left ventricular mass and lower



Thorax Bmj Com Content Thoraxjnl 25 1 79 Full Pdf




Long Term Results Of Aortic Valve Regurgitation After Repair Of Ruptured Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery
Ht 160 Age Mean 95th %ile 2 SD 3 SD 4 SD 15 yrsOnary sinus (70–90%), less commonly from the noncoronary sinus (10–%), and rarely from the left sinus (< 5%) 4–6 Keywords aortic root, aortic sinuses, cardiovascular MRI, cine MRI, sinuses of Valsalva DOI/AJR Received September 2, 09;The size and shape of the patch were designed to restore the normal noncoronary ring and sinus of Valsalva aneurysm implication for surgical treatment J Cardiovasc Surg 1995; 3 Takach TJ, Reul GJ, Duncan JM Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm or fistula manage



1




Back To The Basics Aortic Valve Anatomy
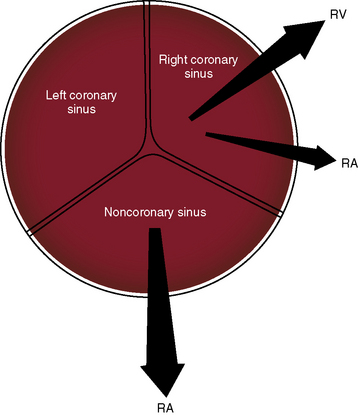
Vol 23 (8)However, accepted upper limits adjusted for body surface area in men is 4 cm and 36 cm in women 2 Anatomically the left coronary sinus is inThe aortic sinuses are in the aortic root, above the heart An aortic sinus is one of three openings, or dilations, that occurs on the inner wall of the ascending aorta, also called the aortic root Each sinus can also be called sinus of Valsalva, sinus of Morgangni, and Petit's sinus The sinuses serve as critical pathways for the two coronary



1




Back To The Basics Aortic Valve Anatomy
· a dilated aortic sinus Valsalva of 42cm I am anxious that this means an operation Everything else was within normal measurements · Discussion Roman et al 2 demonstrated, in a series of 135 normal adults and 52 children, that TTE measurements at the sinuses of Valsalva correlated closely with the BSA in the children, moderately in the adults aged ≥40 years, and weakly in the older adults Gender influenced the AR size at all levels, and although the indexed dimensions were not statisticallyAneurysms of the Valsalva sinuses may be defined as enlargement of the aortic root region between the aortic annulus and the sinotubular junction 1 Diameters of the sinuses varies by age and gender;



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 09 3570




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
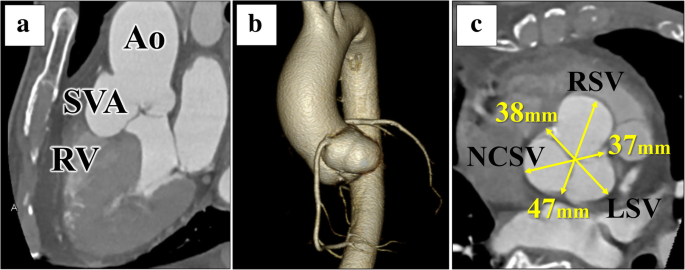
She was found to have a dilated aortic root (Figure 1) measuring 41 cm at the Sinuses of Valsalva, with normal left ventricular function and no aortic regurgitation Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Steady State Free Precession cine imaging revealed an aneurysm of the left sinus of Valsalva measuring ×19 cm (Figure 2), but the location of the · CT of the aortic root demonstrated an aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva The noncoronary sinus extended into the right atrium with what appeared to be a thrombus at the base Fig Cardiac MRI confirmed the presence of an aneurysm of the right and noncoronary sinus although the morphology and dimensions of the ascending aorta and the aortic · Sinus of Valsalva (R 2 model = 044) Age (per 10 years) 06 002




References In Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A State Of The Art Imaging Review Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




Echo Reference Values Kitty Katz Md
An aortic sinus, also known as a sinus of Valsalva, is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic valve Structure There are generally three aortic sinusesThere are usually no signs of an aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva, and it may not be discovered until it ruptures The sinus of Valsalva, more readily known as the aortic sinus, refers to the three pouches behind the valves of the heart, known as the semilunar valves, which come from the aorta These pouches catch the blood that comes back into the heart and cause the valves to closeAortic sinus aneurysms are usually clinically silent un til rupture The most common age for rupture is from puberty to age 30 The presentation of a patient with a ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm depends upon the size of the rupture, the receiving chamber, and any associated anomalies The common symptoms are the abrupt onset




Aortic Education The Marfan Diary



Normal Size
· what are aortic root (at sinuses of valsalva) and mid ascending aorta mri upper normal limits sizes for 58 years old men with bsa 212 and 6 feet tall?Počet řádků 72 · Normal Values of the sinus of Valsalva gender f; · The function of the normal sinuses is to prevent occlusion of the coronary artery ostia during systole when the aortic valve opens The normal sinus diameter is less than 40 cm for men and 36 cm for women Sinus of Valsalva aneurysm can be either congenital or acquired




Normal Limits In Relation To Age Body Size And Gender Of Two Dimensional Echocardiographic Aortic Root Dimensions In Persons 15 Years Of Age Thoracic Key



Marfan Syndrome Aortic Root Dimensions
NORMAL AORTIC ROOT AND ASCENDING AORTA The proximal ascending aorta attaches to the left ventricle at the annulus (hinge line of the aortic leaflets) and includes the aortic root (comprised of the three sinuses of Valsalva), the sinotubular junction, andFig 1 —Coronal oblique CT angiographic image of healthy 64yearold man depicts ascending aortic anatomic landmarks that are typically reported for measurement purposes Measurements are typically reported at aortic annulus (solid black line), aortic sinuses of Valsalva (solid white line), sinotubular junction (dashed black line), mid ascending aorta (dashed white line), and high · According to current American and European guidelines, an aortic size of approximately 19– cm/m 2 indexed to BSA may be considered the upper limit of normal aortic size measured at sinuses of Valsalva1 3 4




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A Review With Perioperative Considerations Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia



Echocardiometric Evaluation Of Cardiovascular Abnormalities In Marfan Syndrome
The sinuses of Valsalva, also known as aortic sinuses, are the anatomic spaces at the aortic root bounded internally by the aortic valve leaflets and externally by outward bulges of the aortic wall The normal sinus diameter upper limit is usually taken as 40 mm (with some publications suggesting 36 mm for females) 1 In typical anatomy, there are three sinuses




Comparability Of Different Z Score Equations For Aortic Root Dimensions In Children With Marfan Syndrome Cardiology In The Young Cambridge Core




Table 3 From Aortic Root Dilatation At Sinuses Of Valsalva And Aortic Regurgitation In Hypertensive And Normotensive Subjects The Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network Study Semantic Scholar




Aneurysm Of Sinus Of Valsalva Wikipedia




An Extracardiac Unruptured Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Complicated With Atherothrombosis In Echo Research And Practice Volume 3 Issue 1 16




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Measurement Of Aortic Root Dimensions By Transesophageal Echocardiography In Adult Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery Maisat W Sawasdiwipachai P Aroonrat W Lapmahapaisan S Ann Card Anaesth




Nomograms For Aortic Root Diameters In Children Using Two Dimensional Echocardiography American Journal Of Cardiology




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Rupture Associated With A Ventricular Septal Defect The Importance Of Multi Angle Assessment By Intraoperative Transesophageal Echocardiography Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia




Long Term Results Of Neomedia Sinus Valsalva Repair In 4 Patients With Type A Aortic Dissection The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery




The Geometrical Modeling Of Aortic Root Complex Ugurlucan M Beyaz Mo Oztas Dm Ozturk A Sahinoglu K Alpagut U Bozbuga N Heart Views



Asecho Org Wp Content Uploads 18 08 Wftf Chamber Quantification Summary Doc Final July 18 Pdf



Www Mdpi Com 75 4418 11 2 2 Pdf



2




A Comparison Of Aortic Root Measurements By Echocardiography And Computed Tomography Sciencedirect




In Vitro Evaluation Of A New Aortic Valved Conduit The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery



Www Ajconline Org Article S0002 9149 12 2 Pdf




References In Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms A State Of The Art Imaging Review Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography




Diseases Of The Great Vessels Ppt Video Online Download




Reference Values Of Aortic Root In Male And Female White Elite Athletes According To Sport Circulation Cardiovascular Imaging



Valve Sparing Aortic Root Surgery From Revolution To Evolution Harky Journal Of Visualized Surgery




Automatic Measurement Of The Sinus Of Valsalva By Image Analysis Sciencedirect




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms Review Of The Literature And An Update On Management Weinreich 15 Clinical Cardiology Wiley Online Library



Www Asecho Org Wp Content Uploads 15 01 15 Thoracic Aorta Pdf



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 09 3570



Congenital Aneurysms Of The Sinuses Of Valsalva Thoracic Key




Table 3 From Gender Age And Body Surface Area Are The Major Determinants Of Ascending Aorta Dimensions In Subjects With Apparently Normal Echocardiograms Semantic Scholar




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques




Diseases Of The Great Vessels Ppt Video Online Download



Sinus Of Valsalva Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Discrepancies In Measurement Of The Thoracic Aorta Jacc Review Topic Of The Week Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology



Www Asecho Org Wp Content Uploads 18 01 Shah Pregnancy And Heart Disease Pdf




Table 1 From Aortic Root Dilatation At Sinuses Of Valsalva And Aortic Regurgitation In Hypertensive And Normotensive Subjects The Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network Study Semantic Scholar



1




How To Master Aortic Measurements With These 5 Techniques
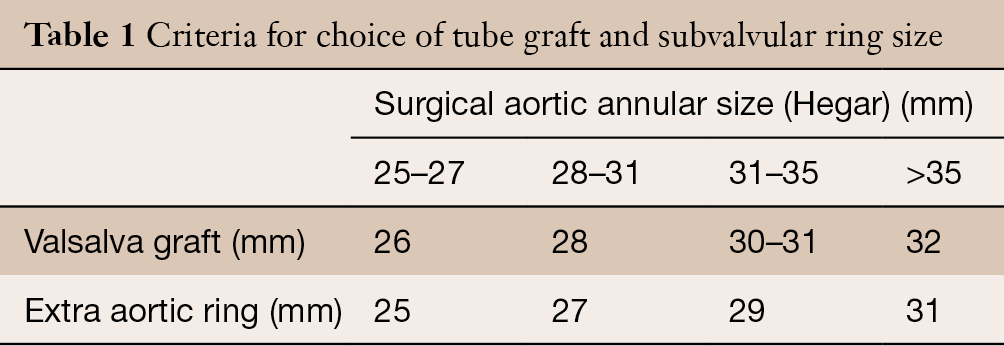



Bicuspid Aortic Valve Repair Adapted To Aortic Phenotype Zakkar Annals Of Cardiothoracic Surgery
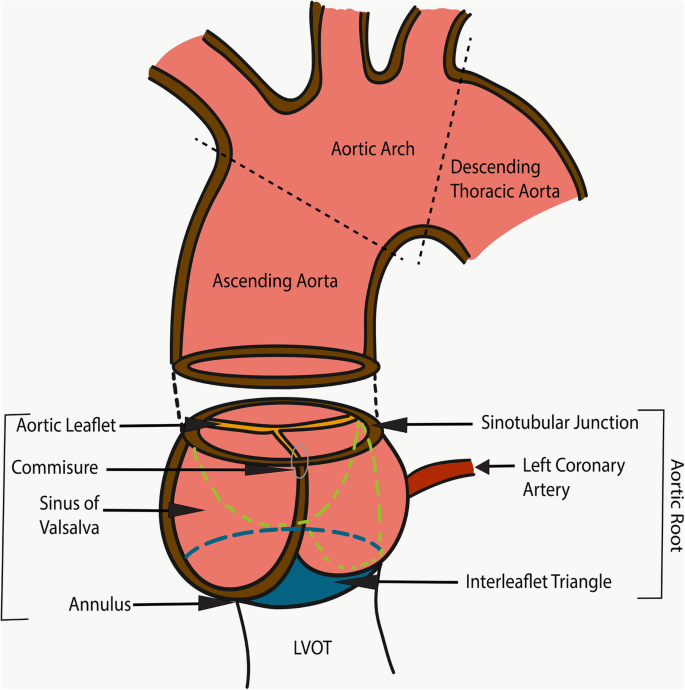



Imaging Of The Aortic Root On High Pitch Non Gated And Ecg Gated Ct Awareness Is The Key Insights Into Imaging Full Text



Multi Detector Ct Angiography Of The Aortic Valve Part 1 Anatomy Technique And Systematic Approach To Interpretation Hoey Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery




Aortic Sinus Diameter In Middle Age Is Associated With Body Size In Young Adulthood Heart




Normal Aortic Root Size Dr S Venkatesan Md



On The Case Radiology Today
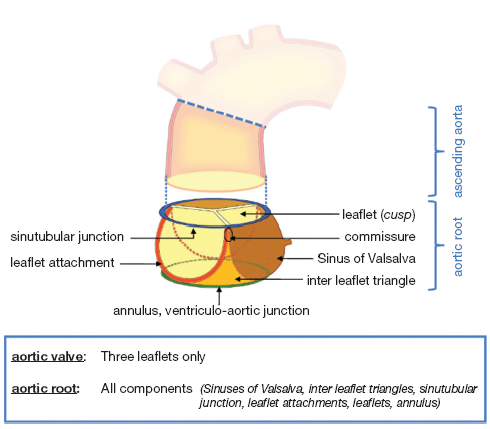



Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Implications For Valve Sparing Surgery Charitos Annals Of Cardiothoracic Surgery




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
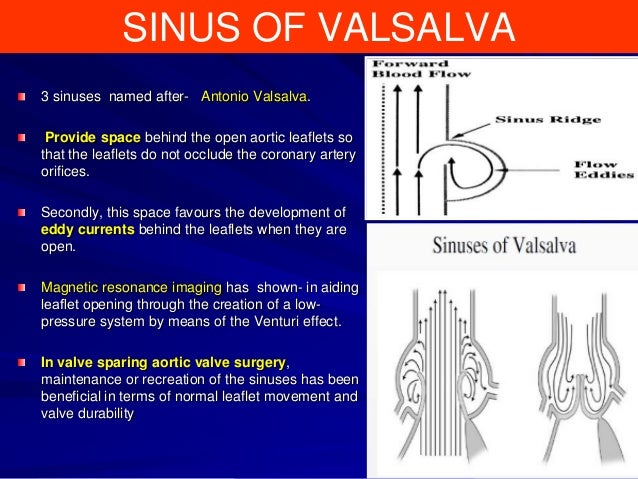



Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm




Normal Limits In Relation To Age Body Size And Gender Of Two Dimensional Echocardiographic Aortic Root Dimensions In Persons 15 Years Of Age Abstract Europe Pmc




Aortic Sinus Diameter In Middle Age Is Associated With Body Size In Young Adulthood Heart




Fate Of Nonreplaced Sinuses Of Valsalva In Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery




Pdf Normal Values Of Aortic Root Dimensions In Healthy Adults




Table Iv From Two Dimensional Echocardiographic Aortic Root Dimensions In Normal Children And Adults Semantic Scholar




Diameter And Growth Rate Of The Thoracic Aorta Analysis Based On Serial Computed Tomography Scans Chang Journal Of Thoracic Disease




Diseases Of The Great Vessels Ppt Video Online Download



Http Pdf Posterng Netkey At Download Index Php Module Get Pdf By Id Poster Id



1




Measurement Of Aortic Root Dimensions By Transthoracic Echocardiogram In Normal Indian Population Venkatesan S Kumar G P Nenwani D Swaminathan N Shankar G R Paul G J J Indian Acad Echocardiogr Cardiovasc Imaging




Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms Review Of The Literature And An Update On Management Weinreich 15 Clinical Cardiology Wiley Online Library



Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Rupture Of Aneurysm Of The Sinus Of Valsalva Presenting As Cardiogenic Shock And Severe Ischemia
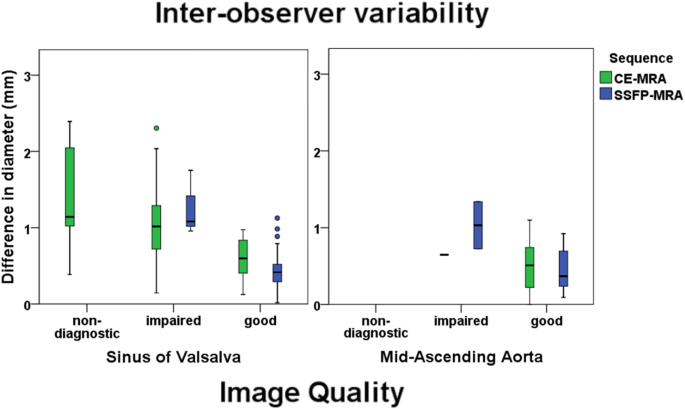



Validation Of Thoracic Aortic Dimensions On Ecg Triggered Ssfp As Alternative To Contrast Enhanced Mra Springerlink




Aortic Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
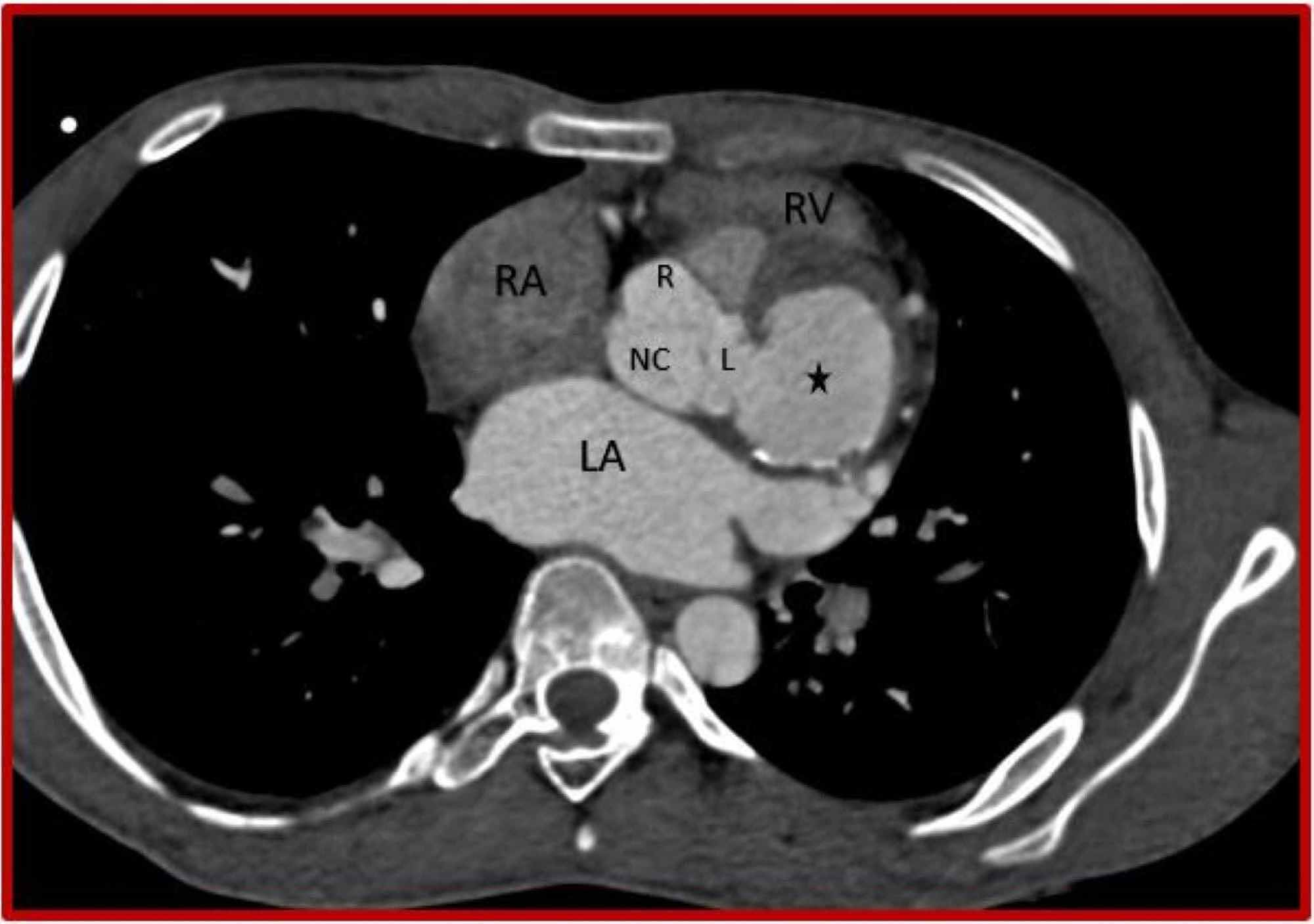



Cureus Rupture Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm Into Interventricular Septum Role Of Cardiac Ct
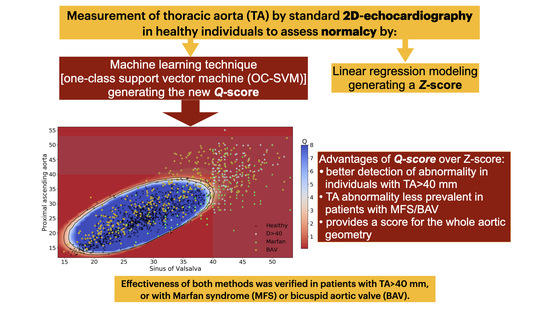



Diagnostics Free Full Text Two Dimensional Aortic Size Normalcy A Novelty Detection Approach Html
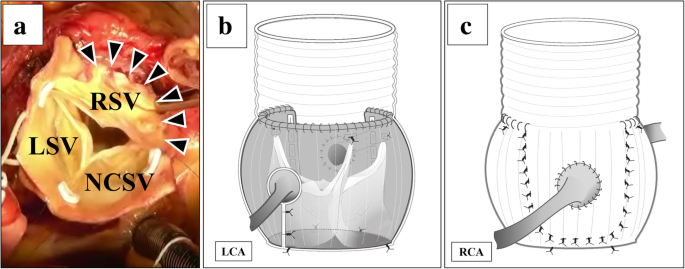



Florida Sleeve Technique For A Right Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysm A Case Report Surgical Case Reports Full Text




Pre And Postoperative Imaging Of The Aortic Root Radiographics




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Academic Oup Com Ejcts Article Pdf 55 6 1211 Ezy437 Pdf
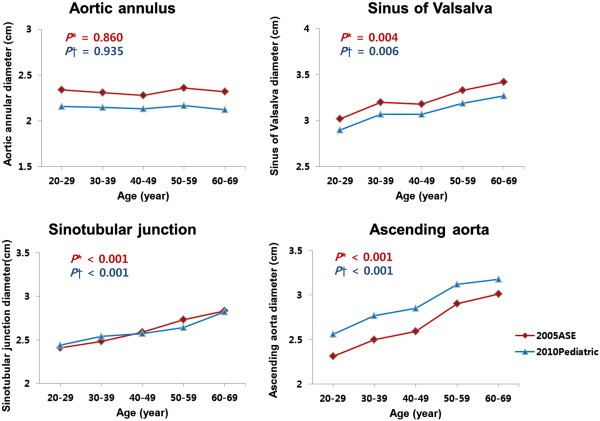



Comparative Measurement Of Aortic Root By Transthoracic Echocardiography In Normal Korean Population Based On Two Different Guidelines Cardiovascular Ultrasound Full Text




Correlating Possible Predisposing Demographics And Systemic Conditions With The Aortic Root Fakoya Ao Otohinoyi Da Omole Ae Oladele C Kalejaiye A Onuegbu A Nwalie E Talukdar D Erinkitola O Ann Afr




Pdf The Aortic Annulus Sinus Of Valsalva Ascending Aorta And Z Score Values In Healthy Children




Relationships Between Age And Maximum Diameter Of Sinuses Of Valsalva Download Scientific Diagram
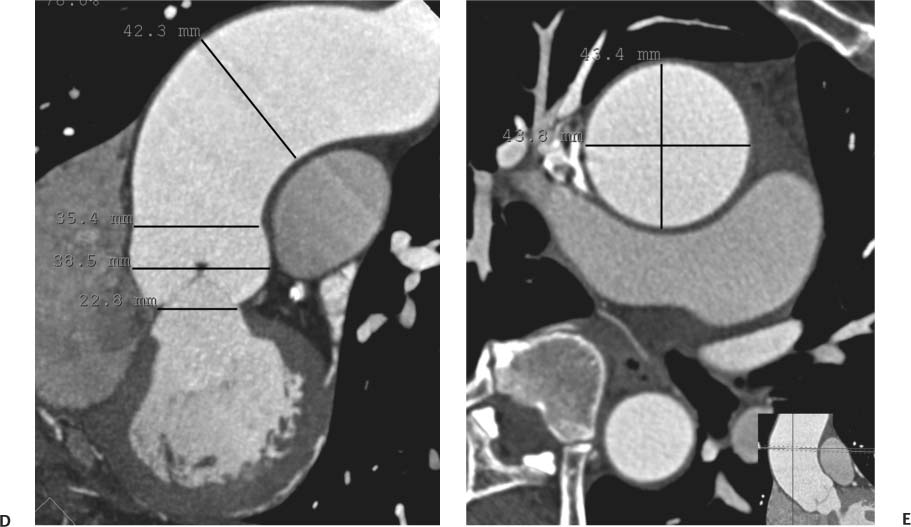



Thoracic Aorta Radiology Key




Nomograms For Aortic Root Diameters In Children Using Two Dimensional Echocardiography Thoracic Key




Determining The Normal Aorta Size In Children Radiology




Aortic Disease Exercise Athletic Participation




Aortic Root Dilatation At Sinuses Of Valsalva And Aortic Regurgitation In Hypertensive And Normotensive Subjects Hypertension




Covariates Of The Sinus Of Valsalva Diameter And Height Identified In Download Scientific Diagram




Diseases Of The Great Vessels Ppt Video Online Download




Aortic Root Dilatation At Sinuses Of Valsalva And Aortic Regurgitation In Hypertensive And Normotensive Subjects Hypertension




Univariate Covariates Of The Sinus Of Valsalva Diameter And Height Download Table
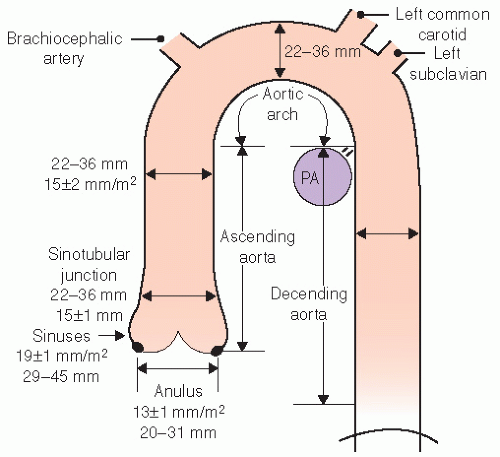



Diseases Of The Aorta Thoracic Key




10 Accf Aha ts Acr Asa Sca Scai Sir Sts Svm Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease Circulation




Biomechanical Properties And Histological Structure Of Sinus Of Valsalva Aneurysms In Relation To Age And Region Sciencedirect




Ppt Sinus Valsalva Asymmetry Is The Normal Aortic Root Anatomy Powerpoint Presentation Id


コメント
コメントを投稿